

ANNEX 3 GUIDANCE ON REVIEW/APPROVAL OF RISK-BASED SHIP DESIGN
1. Application
(1) This guidance is to be applied to risk-based approach and risk-based approval procedure which serve to review/approve innovative ship design of novel concept that deviated from existing pre- scriptive regulations and rules.
(2) The risk-based approval procedure is to take into account relevant risk which can occur during the whole life cycle of the ship in course of design, construction, operation and demolishment.
(3) Approval criteria are to be newly defined in terms of risk on the basis of the submitted design
in risk-based approval process. Accordingly, design analysis and result reviews are to be carried out. Therefore, whenever the content of the target design changes, approval criteria are to be newly defined in risk-based approval process. However, the intentional changes to lower risk levels related to operation and work procedure are not allowed.
(4) Risk-based approach and risk-based approval procedure defined in this guidance may be appli- cable to all areas related to ship design, but are not limited to the specific technical, regulatory fields.
(5) For successful application of this guidance, all stakeholder are to exchange their opinions from the start of design to final approval through continuous mutual discussion.
(6) Class Notation specified by the Society may be considered given to the ship designed and ap-
proved based on this guidance.
2. Definitions
The definitions of terms used in this guidance are as follows;
(1) Risk-based design is a methodology that integrates probabilistic and risk-based approaches in the design process of individual ship design and ship system design.
(2) Risk-based approval is to review and approve ships on which innovative novel design or
risk-based design has been applied.
(3) Design team is responsible for novel design or risk-based design. Members may include owner, designer, builder, manufacturer and expert group in charge of design concept, generic design and specific design.
(4) Approval team approves novel design or risk-based design. Members may include person in charge of risk-based design approval in the Society, expert group assigned by the Society for risk-based design approval and surveyor in charge of target ship.
(5) General design refers to a design at a level where at least an estimate may be possible. The primary systems and target functions are to be defined definitely. Shape of the ship, subdivision, structure, material, dimension, arrangement and specification of primary system, realize method of target function and operation characteristics etc. shall be included in the general design.
(6) Specific design refers to a design at a level where purchase, manufacture and installation may be possible. All details concerning construction of target ship are to be completed, and all in- formation related to installation or operation is to be specifically identified. In addition to the completed generic design, the specific design complies with the results of the generic design with respect to specific dimension of all structures, detailed arrangement and specification of all
installed equipment, detailed specifications methods, etc.
(7) Validity demonstration of design is to
functions. The main works are to confirm the identified required requirements.
of related components, construction methods, work
confirm realization possibility for intentive target operating risk-based approval procedure and to meet
(8) Functional requirements are needed to realize target functions of design.
(9) Safety demonstration of design is to confirm that risks of design are at risk acceptance level.
Risk levels are estimated through risk analysis. Comparing them with risk evaluation criteria, en- sures that safety is demonstrated.
(10) Safety requirements are necessary to ensure/maintain the safety of design.
(11) Survey requirements refer to an assortment of surveys, checks, monitors, maintenance, tests, etc. during construction/operation; the least restrictions necessary to continually ensure/maintain
![]()
Guidance for WIG ships(Wing-In-Ground Effect Ships) 2012 61
![]()
safety level confirmed by final approval, related to construction, manufacture, and operation phases of design target.
(12) High level safety means overall safety level for the ships, which is a result achieved by total
calculation of possible risks on components(all systems and functions) of ships.
(13) Low level safety means a safety level regarding specific components of ships. This is limited to specific main system, sub-systems, equipment, parts, functions, etc. and is a result of separate
and independent calculation.
3. Approval procedure
(1) Risk-based approval procedure is intended for validity/safety demonstration of target design,
which especially focuses on design stage. It consists of three steps of
proval for construction and monitoring inspection. (See Fig 1.)
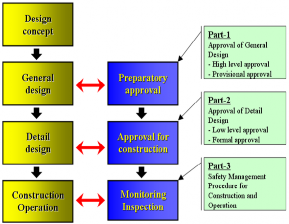
Fig 1. The stage of approval procedure
(2) The design stage is subdivided into ‘design concept’, ‘generic design’, linked with preparatory and final approval stages. Risk-based approval sign is to be carried out through preparatory approval and the same carried out through final approval.
preparatory approval, ap-
‘specific design’. It is on safety in generic de- in detail design is to be
(3) The risk-based requirements are identified by preparatory and final approval procedure. They are means of controlling risks of the ships and they are to be reflected directly to general design and detail design.
(4) Risk-based survey requirements are prepared by requirements on construction/operation through
preparatory and final approval procedure. It is the core of safety management system which is standards of works, monitors, surveys, audits, controls during construction/operation.
(5) The entire structure, primary, stages and the order of preparatory and final approval procedure is
specified as Fig 2.
![]()
62 Guidance for WIG ships(Wing-In-Ground Effect Ships) 2012
![]()
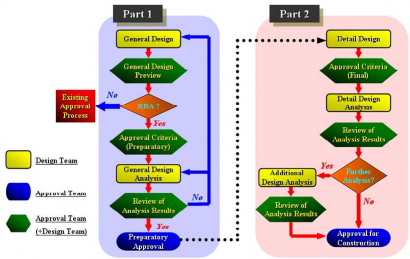
Fig 2. The structure of preparatory, final approval procedure
4. Preparatory approval
(1) Preparatory approval is a validity approval procedure on generic design, the approval procedure is specified as Fig 3.
order of preparatory
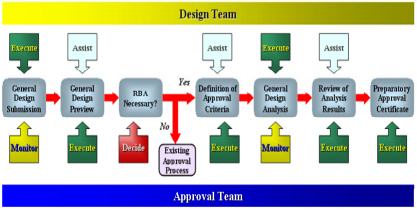
Fig 3. Preparatory approval procedure flow
(2) Submission of generic design
(A) The design team is to prepare novel design or risk-based design, submit ments to the approval team.
it and related docu-
(B) The subject vessel, shape of the ship, subdivision, structure, material, dimension, arrangement
of primary system, boundary condition, specification, realizing methods of target function and operation characteristics shall be included in generic design.
(C) The design team is to consider existing prescriptive regulations, rules and standards.
(D) If necessary, terms and definitions concerning design and approval procedure are to be de- fined at the initial stage. The definition of these terms increases efficiency by avoiding misinterpretations and confusion.
(3) Preview of generic design
(A) The approval team previews the submitted generic design with respect to safety of life and environment protection, and understands clearly the characteristics of the target design. The
team considers if risk-based approval procedure is to be applied according to the novelty of
design specified by Table 1.
![]()
Guidance for WIG ships(Wing-In-Ground Effect Ships) 2012 63
![]()
Table 1 Approval matrix by design novelty
Category | Novelty 1(2) | Novelty 2(3) | Novelty 3(3) | Novelty 4(4) |
Risk Assessment | Not required | Required (partly) * Violation of primary regulations * Depending on risk assessment outcome * Semi quantitative risk assessment on hazards medium or high(5) | Required (partly) * Quantitative risk assessment on hazards medium or high(6) | Required (overall) * Quantitative risk assessment on all hazards(6) |
Qualifications of a design team | Not required | Required * Design, operational experience experts * Individuals having general knowledge of risk assessment | Required * Design, operational experience experts * Risk assessment experts | Required * Design, operational experience experts * Risk assessment experts |
Applicable regulations | *Existing prescriptive regulations and rules | * Existing prescriptive regulations and rules * Parts of risk-based approval procedure * Applicable standards if available from other industrial sectors | * Risk-based approval procedure * Applicable standards if available from other industrial sectors | * Risk-based approval procedure |
Surveys | *Existing regulations of surveys | * Internal surveys * Additional surveys at related safety events | * Internal/external surveys * Additional periodic surveys at hazards | * Continuous monitoring and reporting |
Notes : (1) Categorization of design novelty (2) ‘Novelty 1’ refers to a conventional design. Risk-based approval procedure is not to be applied. Therefore existing prescriptive regulations, rules and standards may be applied. (3) ‘Novelty 2-3’ correspond to the middle level not belonging to Novelty 1&-4 and may take existing approval procedure and risk-based approval procedure depending on the situations. Basically, they follow existing appro- val procedure according to design and may apply risk-based approval procedure only for important part sys- tems and functions. If necessary, they may apply risk-based approval procedure for overall design. (4) ‘Novelty 4’ is to follow risk-based approval procedure except exceptional cases. As it is a totally new con- cept, there are neither past buiding experiences, nor, applicable existing prescriptive regulations, rules and standards. (5) Semi-quantitative risk analysis and assessment are methods of quantitative estimates. They defines indexes on frequency and consequences of accidents in advance, giving an index of the most appropriate grade. (6) Quantitative risk analysis and assessment are is methods completely estimating quantitative values. It estimates frequency and consequences of accidents in specific numbers through records, experiments, calculations, simu- lation tests etc. (7) If risk levels may be confirmed by qualitative risk analysis and assessment, quantitative risk analysis and as- sessment may be optionally or additionally carried out. | ||||
Category | Proven(1) | Limited field history(2) | New or unproven(3) |
Known | 1 | 2 | 3 |
New | 2 | 3 | 4 |
(B) The approval team investigates comprehensively existing prescriptive regulations, rules and standards which may affect design, identifies primary items on preparatory approval criteria, relating plans and contents.
(C) The approval team discusses the contents of the submitted generic design. A design team assists in the preview work.
(D) If risk-based approval procedure is decided not to be applied by an approval team, existing
prescriptive regulations and rules may be applied to approve.
(4) Definition of preparatory approval criteria
![]()
64 Guidance for WIG ships(Wing-In-Ground Effect Ships) 2012
![]()
(A) The approval team is to define the required conditions and formal procedures based on the results on preview discussion of generic design.
(B) The specifications are to be included in preparatory approval criteria as follows: It may be
noted that additional items may be required should other situations arise.
(a)
Definition of main risk concerned, and its evaluation criteria
(b) HAZID plans (including methods and scopes)
(c)
Risk analysis and assessment plans (including methods and scopes)
(d) Work plan for generic design analysis such as experiments, calculations, analysis, simu- lation tests etc. (including methods and scopes)
(e)
(f)
Functional requirement and safety requirement list (Draft requirements) Assumptions, exemptions, restrictions
(C) The approval team defines preparatory approval criteria to advise the design team.
Preparatory approval criteria are to be defined by discussions led by the approval team.
(D) The followings agenda is to be discussed in preparatory approval criteria meeting.
(a)
Design concepts
(b) Design objectives
(c)
Design novelty
(d) Risk-based features in design
(e)
(f)
Violations and potential violations related to the existing prescriptive regulations, rules and standards etc.
The deficiencies or limitations of existing prescriptive regulations, rules and standards
(g) Potential hazards which may happen to all systems and functions of ships
(h) Necessary items to realize target functions.
(E) Proper kinds of risk-based or reliability analysis methods are to be identified by risk analy-
sis and assessment plans. The features, limitations, application methods etc. are to be defi- nitely mentioned.
(F) Proper experiments, theoretical analysis and calculations, possible simulation tests are to be
identified in general design analysis plans. The features, limitations, application methods etc. are to be definitely mentioned.
(G) General design analysis plans may be changed by results of general design analysis and
they are to be reflected to specify design analysis plans.
(H) Risk of major interest is to be identified, proper evaluation criteria corresponding to the risk are to be defined and identified.
(I) Objective safety level for existing prescriptive regulations, rules and standards etc. may be
referred to define risk evaluation criteria. Available risk evaluation criteria in other industrial sectors may be referred to. However, an approval or design team is to newly develop spe- cific risk evaluation criteria in case of novel design.
(5) Analysis of general design
(A) The design team is to analyse risks involved in generic design relating to preparatory appro- val criteria under the supervision of the approval team. The team identifies design items
which require specific analysis, carries out experiments, calculations, analysis and simulation
tests etc.
(B) If necessary, analysis results of general design may be utilized to risk analysis works again and risk assessment is to be carried out by preparatory approval criteria. Safety of general design is to be judged.
(C) Hazards identification is to be included in risk analysis works. Besides, other risk analysis methods such as FSA, FMECA, HAZOP, FTA, ETA, RBD, Markov model, Bayesian net- work, structural reliability analysis etc. may be applicable.
(D) The design team is to carry out hazards identification on novel design or risk-based design.
Related hazards and consequences are to be identified, also safety systems(accident pre- vention and mitigation measures) are to be found. Through procedure, the requirements are to be identified to ensure or improve the design safety. Preparatory approval criteria are to be revised. General hazards identification flow is specified as Fig 4.
![]()
Guidance for WIG ships(Wing-In-Ground Effect Ships) 2012 65
![]()
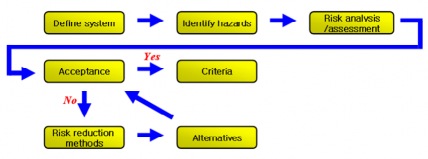
Fig 4. Hazards identification flow
(E) The design team is to carry out risk assessment at the end, after preparing risk model based on risk analysis results. Risk control measures are to be prepared according to risk assess- ment results and risk evaluation criteria defined in preparatory approval criteria.
(F) The specifications to be considered in risk assessment works are as follows:
(a)
Identified hazards, frequency, consequence
(b) Safety systems included in the design which may be identified
(c)
Risk model for quantitative risk analysis
(d) Reference, assumption, uncertainty, sensitivity etc.
(e)
(f)
Comparison of the calculated risk levels and evaluation criteria Risk control measures and risk reduction level
(g) Items which need additional risk analysis, experiments, calculations, analysis, simulation
tests.
(h) Notices related to construction, operation
(G) Documents related to procedures and results are to be properly prepared, because risk as- sessment results are the most important data for preparatory approval.
(6) Review of analysis results for general design
(A) The approval team is to review hazards identification results and confirm the following specifications as specified for reasonable procedures, results of general design.
(a)
Appropriate qualifications of participants
(b) Keep standards of hazards identification works(eg. IMO FSA guidances).
(c)
Whether the rank of identified hazards considered proper.
(d) Whether the identified safety systems reflect to the design proper.
(e)
(f)
Whether features of novel design or risk-based design reflected to identified hazards and safety systems proper.
Whether if necessary, preparatory approval criteria revised according to identified design requirements.
(B) The approval team reviews the adequacy of risk model
(C) The approval
(D) The approval
team reviews the adequacy of risk assessment results.
team reviews reasonable risk reduction level in case a design team applies risk
control measures.
(E) The approval team reviews the adequacy of experiments, calculations, analysis, simulation tests etc and the results of them.
(7) Issuance of preparatory approval certification
(A) The approval team is to review the analysis results for generical design in accordance with
preparatory approval criteria and decide
issuance of preparatory approval certification after
judging realization possibility and safety level of general design. The certification is not to be issued until all hazards, faults related to general design are identified and their control is demonstrated.
(B) The approval team is to consider the following specifications to issue preparatory approval certification.
(a)
Possible to realize general design
(b) May all identified and calculated risk levels be acceptable
(c)
Are there omitted or ignored risks
(d) Comply with design requirements
(e)
Is risk reduction level by risk control measures reasonable
(C) It is noted that preparatory approval certification is not guaranteed for final approval. It is
![]()
66 Guidance for WIG ships(Wing-In-Ground Effect Ships) 2012
![]()
only possible through the final approval.
(D) The form of preparatory approval certification is to be in accordance with the Guidance re- lating to the Rules.
5. Final approval for construction
(1) Final approval is procedures of detailed design preparation and analysis. The procedure is speci- fied as in Fig 5.
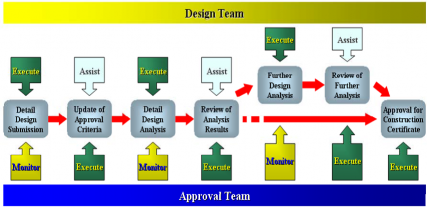
Fig 5. Final approval procedure flow
(2) Submission of detailed design
(A) The design team submits specific design to the approval team. The design reflects risk con- trol measures, which are identified or created in preparatory approval procedure, in accord-
ance to the analysis results for general design.
(B) Detailed design is to include all details not defined in general design specifically. For exam-
ple, detailed structural arrangement and the shape in all parts of the ships, dimension of all structures, construction method, detailed layout and final specification of all equipment sys- tems, specification and installation information of all equipment, operating conditions with all purposes and related loads, operating system, detailed information etc. related to propulsion and maneuver shall be developed in detail design.
(3) Renewal of final approval criteria
(A) The approval team is to identify the differences between basic and detailed design based on detailed information by detailed design as well as additional, detailed design information and revised design contents. The team is to define necessary requirements and formal procedure for final approval.
(B) Final approval criteria are intensified and expanded types of preparatory approval criteria. In other words, general items which are considered in preparatory approval criteria are same as in final approval criteria. Preparatory approval criteria stated requirements which shall be complied with for approval are to be written in detail in final approval criteria.
(C) Items not recorded in preparatory approval criteria may be identified newly in detailed design. Risk evaluation criteria, detailed design analysis plans, the other requirements etc. of
newly identified items are to be added to final approval criteria.
(D) If necessary, operation methods related to experiments, calculations, analysis, simulation tests etc. on risk analysis, assessment and detailed design in final approval criteria may be as-
signed by approval team additionally.
(4) Analysis of detailrd design
(A) The design team is to identify risks related to detailed design in accordance with final ap- proval criteria, carry out accompanied experiments, calculations, analysis, simulation tests etc. The team is to submit proper documents on the results of detailed design analysis to the approval team.
(B) The approval team is to supervise frequently that the design team carries out detailed design analysis suitably by final approval criteria. The representative in the approval team may at- tend the meeting of the design team.
(C) In case contents of basic design in detailed design stage are changed, hazards identification,
![]()
Guidance for WIG ships(Wing-In-Ground Effect Ships) 2012 67
![]()
analysis and assessment are to be carried out again overall.
(5) Review of analysis results for detailed design
(A) The approval team is to review that experiments, calculations, analysis, simulation tests etc. related to detailed design are to be carried out reasonably, clearly as well as the results.
(B) The list of requirements for final approval is to be prepared by the results of preparatory approval criteria, final approval criteria, basic design and detailed design analysis. The fol-
lows as specified are to be included to issue final approval certification.
(a)
Possible risk categories and risk evaluation criteria
(b) Reasonable bases on limitations and restrictions applied to risk analysis
(c)
Requirements
to meet applied assumptions and conditions for identifying risks
(d) Requirements
for successful functions of safety systems and risk control measures
(e)
Requirements
for achieving target functions of design
(f)
If necessary, verifications for demonstrating satisfaction of requirements above.
(C) Items recorded with list of requirements for final approval are related with the follows as specified directly, they are draft requirements of construction and survey related to operation.
(a) Related to construction : safety and quality management requirements related to con- struction, manufacture and installation etc.
(b) Related to operation : restrictions, maintenance requirements, procedure during operation.
(6) Issuance of final approval certification
(A) The design team is to submit all necessary documents (specifications, drawings, calculations etc.) to the approval team prior to issuance of final approval certification. Basically docu- ments related to detailed design, analysis shall be submitted, relevant document list to be
submitted may be adjusted by an agreement between the design team and approval team.
(B) All possible hazards of novel design or risk-based design are to be identified to issue final approval certification, they are to be reflected to risk analysis and assessment. What all risks
are within risk acceptance level shall be verified comparing all risks with all risk evaluation
criteria. Developed detailed design which may carry out sufficiently target functions are to be verified.
(C) The approval team is to confirm the list of requirements for final approval and the suit-
ability of the design. The team is to decide issuance of judging detailed design or realization possibility of the
acceptable.
final approval certification after target design, safety level are
(D) Commencement of construction and manufacture may be possible after issuance of final ap- proval certification. In other words, final approval is a formal and final design approval pro-
cedure to verify safety and adequacy on entire design including basic design and detailed
design.
(E) The form of final approval certification is to be in accordance with the Guidance relating to the Rules.
6. Survey requirements
(1) The design team is to prepare survey requirements during construction and operation based on identified safety systems, risk control measures, notices, restrictions in final approval procedure. The team is to submit a document of safety management system to the approval team for approval.
(2) Survey requirements during construction are to guarantee that safety level of the proven design by final approval maintains without lowering sufficiently at construction and manufacture proce- dure of ships. The follows as specified are to be considered.
(A) Existing prescriptive regulations, rules and standards related to construction and manufacture
(B) Qualification verification of yards, factories, worker related to construction and manufacture
(C) The adequacy of construction and manufacture process (including restrictions/limitations)
(D) The adequacy of construction and manufacture procedure (including restrictions/limitations)
(E) Notices on quality management procedure of construction and manufacture
(F) Necessities and points of test during or after construction and manufacture
(G) Necessities and points of survey during or after construction and manufacture
(H) Sea trial verifications and points after construction and manufacture
(I) Other related safety systems and procedures
(3) Survey requirements during operation are to guarantee that safety level of the proven design by final approval maintains without lowering sufficiently at operation of built ships and the purpose of providing services. The follows as specified are to be considered.
![]()
68 Guidance for WIG ships(Wing-In-Ground Effect Ships) 2012
![]()
(A) Existing prescriptive regulations, rules and standards related to operation
(B) Qualification verification of complements
(C) Adequacy of sea routes and services (including restrictions/limitations)
(D) Adequacy of operating conditions and procedures (including restrictions/limitations)
(E) Adequacy of necessary work procedures on-board (including restrictions/limitations)
(F) Adequacy of operating procedures for emergency (including restrictions/limitations)
(G) Adequacy
of maintenance procedures by itself during operation (including re-
strictions/limitations)
(H) Verification necessities and points by surveyors during operation
(I) Document requirements to be on-board during operation
(J) Other relevant safety systems and procedures
(4) The safety level of the proven design in final approval procedure is to be kept within an ac-
ceptance level in construction and operation step. It may be possible by safety management sys- tem ultimately. The system integrates quality management procedures, requirements, restrictions, maintenances to keep safety adequacy during ship's construction and operation.
(5) The approval team is to carry out verification of safety adequacy(surveys, checks, audits, mon- itors etc.) according to the approved safety management system. The verification performances and results of safety adequacy are essential to keep certification, this work is to be carried out by traditional surveys and verification procedures similarly.
(6) Periods, scopes and points of verification of safety adequacy are to be as defined by safety management system. Generally verification requirements of safety adequacy may be complicated if features of design are more innovative. The requirements may be reduced if experience on novel design or risk-based design is accumulated and reliability is verified enough.
(7) The design and assumption confirmed in final approval procedure may be changed in con-
struction and operation step. If they affects the risk of the ship, the approval team is to decide
to carry out risk analysis and assessment again. According to the results, survey and safety management system may be revised.
requirements
(8) If necessary, reliability based maintenance procedures on the basis of ship's major system, fail- ure rate of function or reliability may be included additionally.
![]()
Guidance for WIG ships(Wing-In-Ground Effect Ships) 2012 69
![]()
7. Qualification of design/approval team
Category | Main jobs | Qualification | |
Design team | Owner and designer | * Prepare and advise concept of novel design or risk-based design. * Carry out economic evaluation, risk assessment and preparation, analysis, test of all design. | * Past experience related to the characteristics of target vessel or similar experience * Experience applying risk-based approach * Completion of formal relevant education/having qualification |
Yard and manufacturer | * Construct/manufacture ships and equipment which are the purpose of novel design or risk-based design. | * Record of constructed ships and manufactured equipment in the past * Experience on constructed ships similar to target design and manufactured equipment * Ability to meet safety requirements related to construction and manufacture and possible to submit related documents * Understanding on overall safety management system | |
Complements | * Assume overall operation of novel design or risk-based design ships. * Belong to navigating officers, engineer officers, superintendents, rating etc. * Define/perform the overall information on ship's operation in risk-based safety management system. | * General knowledge on risk-based approach * Understanding on safety management system | |
Experts | * Individuals having knowledge and experience enough when participated in | * Whether related qualification * Related experiences and research experiences * Objectively independent position | |
Approval team | Persons in charge of design approval | * Approve risk-based design jobs | * Expert knowledge on risk-based approach and approval procedure * Applied experience on risk-based approach and approval procedure * Research experience on risk-based approach * Past approval on ships similar to target design * Completion of formal relevant education/having qualification |
Surveyors | * Perform survey jobs on applicable laws/regulations/rules/safety management system and issue approval certification. | * General knowledge on risk-based approach * Understanding on safety management system and safety survey tools/methods * Understanding on applicable laws/regulations/rules | |
Experts | * Individuals having knowledge and experience enough when participated in | * Whether related qualification * Related experiences and research experiences * Objectively independent position | |
![]()
![]()
70 Guidance for WIG ships(Wing-In-Ground Effect Ships) 2012
![]()
GUIDANCE FOR WIG SHIPS (WING-IN-GROUND EFFECT SHIPS)
Published by
NO.5, Shabnam. Alley
Qaem Maqam-e-Farahani St., Haft-e-Tir. Sqr, TEHRAN, IRAN
TEL : +98 21 421 6000
FAX : +98 21 8832 4734
Website : http://www.ics.org.ir
![]()
CopyrightⒸ 2012, IRANIAN CLASSIFICATION SOCITY
Reproduction of this Guidance in whole or in parts is prohibited without permission of the publisher.
![]()